Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Agent-Based Management
- Common Tasks
- Data Providers
- Directory Services
- Auditing
- Hosts
- Templates
- Template Properties
- Batch Update Templates
- Assign Templates
- Log Management Templates
- SCAP Compliance Monitor
- Active Directory User Monitor Templates
- File and Directory Monitor Templates
- Windows Monitor Templates
- CPU Monitor Template
- Memory Monitor Template
- Disk Space Monitor Template
- Account Lockout Monitor Template
- Audit Policy Monitor Template
- Logon As Monitor Template
- Logon Monitor Template
- Performance Counter Monitor Template
- PowerShell Template
- Process Monitor Template
- RDP Session Monitor Template
- Registry Value Monitor Template
- Service Monitor Template
- SMART Disk Monitor Template
- System Security Monitor Template
- Windows Update Template
- WMI Query Template
- Task Scheduler Template
- Clock Synchronization Template
- Defragment NTFS Disks Template
- Network and Application Monitor Templates
- SSL Certificate Monitor Templates
- Database Templates
- Email Monitor Templates
- SNMP Monitor Templates
- Windows Accounts Templates
- Monitors
- Reports
- Auto-Configurators
- Filters
- Actions
- Schedules
- Environment Variables
- Options
- SNMP
- SSH Shell
- Syslog
- System Reset
- Shared Views
- Active Directory User and Group Filters
- Assign Actions
- Assign Azure Audit Logs
- Assign Consolidated Logs
- Assign Directories
- Assign Disks
- Assign Event Logs
- Assign Files
- Assign Services
- Assign Shares
- Auto-Config Host Assignment Properties
- Define CSV and W3C Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns
- Define Log Entry Columns with Regular Expressions
- Executable Status
- Executable Timeline
- Explicitly Assigned Logs
- File Explorer
- General Executable Properties
- Report Columns
- Report Date/Time Ranges
- Report Security Event Log Filters
- Select Folder or File
- Target Files and Sub-Directories
- Command Line Interface
- Server Configuration
- Agent Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Best Practices
- Terminology
Getting Started
Corner Bowl Server Manager is a SIEM, a server monitor, an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) and is used to maintain high server availability, automatically respond to threats and fulfill compliance requirements imposed by regulating organizations and governments.
In this Topic
Background
Server Manager was first released back in the mid-1990s as an enterprise network disk monitoring software package, then, in 2001, centralized log management was added. Server Manager is one of the most seasoned SIEM solution on the market today with 22+ years in development and sales.
The SIEM and server management space is constantly evolving. In order to adjust for our rapidly changing environments, implementations and technology updates, Server Manager is constantly updated both with customer driven functionality feature sets, such as Azure Audit Log Consolidation and Linux Agents, as well as the core technologies used to build Server Manager. We pride ourselves on keeping up with the latest technologies, such as .NET 7, while maintaining backwards compatibility for older systems implemented and deployed in static classified air gapped environments.
Environments
Server Manager can be deployed on physical hardware, VMs, Windows Servers, Windows Workstations, Linux (including Red Hat and Ubuntu) and single stand-alone air gapped servers and workstations. Our customer base ranges from large corporate networks with 1000s of managed systems processing over 100 million entries per day, to classified air gapped mission control rooms, to single stand-alone classified air gapped machines required to meet JSIG compliance requirements.
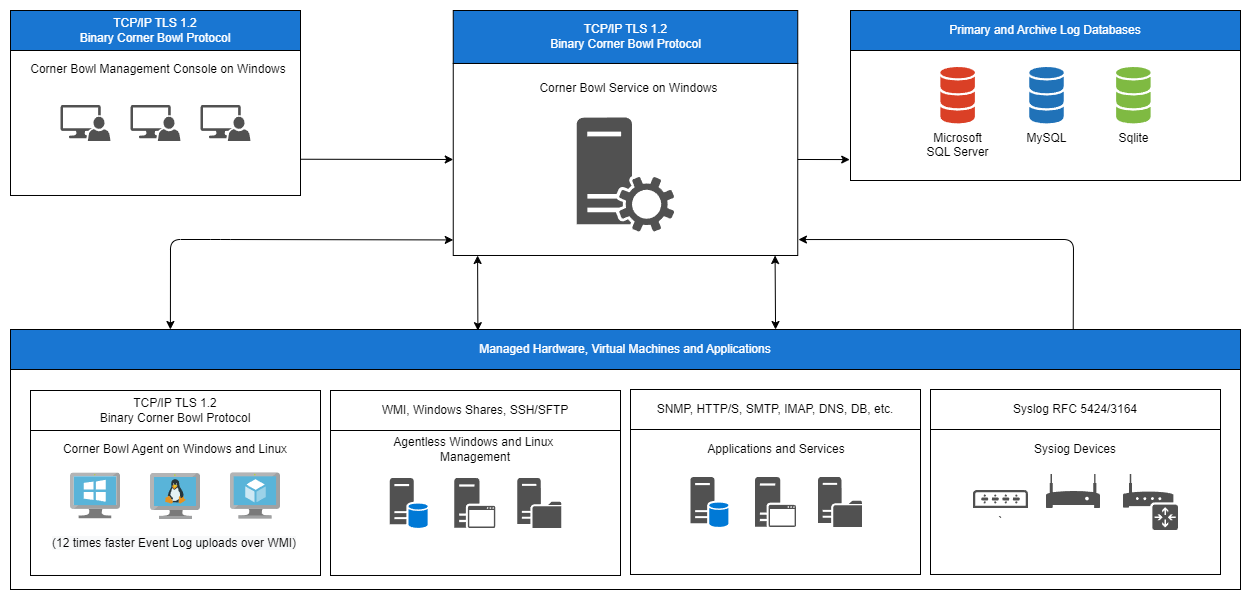
Architecture
Server Manager in configured and managed from a Windows machine then remotely manages machines using native technologies or through our Windows and Linux Agents. We highly suggest you implement our agent-based Windows Services and Linux Daemons. Using our Agents enables you to bypass Windows and Linux Security, minimize Server Manager's footprint on Security and Audit logs, execute local IPS functions directly on managed machines, which is not always possible with native technologies, and lastly, minimize log entry network transmission to mission critical entries.
Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Windows Service | The Windows Service provides all server functionality and does not require agents to be installed on managed machines. |
| Management Console | The Management Console provides the user interface to configure the service and view and search logs. The console connects to the service over TCP/IP port 21843 and can be installed on any Windows machine. |
| Tray Icon | The Tray Icon provides desktop notification messages and like the console can be installed on any Windows machine to receive real-time notifications. |
| Windows and Linux Agent | The Agent optionally installs on remote managed hosts and provides a means to anonymously and reliably upload log entries and files by-passing Windows Security, remote WMI and SSH/SFTP . |
Component and Network Diagram
General Concepts
Hosts are added to the system, then Templates, which contain monitor settings such as the logs and frequency to download, are assigned to hosts. The assignment of a template to a host results in a Monitor being added under the host. Depending on the type of data, Reports either scan Log Databases, Active Directory or summarize monitor results. Auto-Configurators scan Active Directory then automatically add new hosts then assign templates and reports to the new hosts. The Auto-Configurator optionally removes decommissioned hosts.
Data Storage
Data Providers have three purposes:
- To save log entries, PowerShell results, and SNMP Traps to a centralized log database for a period of time such as 1 year.
- To save monitor history for internal review, charting and external BI Dashboards.
- To configure database connections for Database Monitoring Templates.
The following database engines are supported:
- SQLite (Default)
- MySQL
- SQL Server
- Corner Bowl Flat-File Format (Deprecated)